Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid arteries further major blood supply to the brain. These arteries can become narrowed or blocked due to a process called atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries. Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries can occur as we get older, however certain factors will increase the chance of carotid artery disease.
CAD risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- Family history of vascular disease
- Elevated cholesterol levels diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- History of heart disease
- History of vascular disease
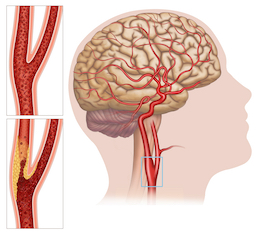
If the blockage in the carotid artery disease becomes severe, it can cause a permanent stroke or a transient stroke, also called transient ischemic attack, TIA. Carotid artery disease is the cause of more than 50% so all strokes in the United States. Strokes are also leading cause of disability in the United States. Strokes can be prevented if carotid artery disease is diagnosed and treated.
Carotid Artery Doctor
If you are having any of these symptoms or any other concerning health condition then you should consult with a carotid artery doctor immediately.
Carotid arteries disease symptoms
Unfortunately the first symptom of the carotid arteries disease is usually a stroke or a transient ischemic attack, TIA.
The symptoms of a TIA or stroke may include:
- Weakness in arms or legs
- Difficulty speaking or getting words out or understanding speech
- Disorientation or difficulty with coordination
- Severe headaches
- Memory loss
- Facial drooping
- Confusion
- Visual disturbances
Symptoms of a transient ischemic attack, TIA, may resolve within 24 hours, however in a case of a stroke the symptoms would be permanent and cause disability for life.
People may have carotid artery disease without any signs of symptoms with asymptomatic stenosis of the arteries these patients are at high risk of developing a stroke in the future.
Asymptomatic stenosis of the carotid arteries can be diagnosed by physical examination then a swishing sound which is called a bruit is heard with a stethoscope over the neck area.
Asymptomatic carotid stenosis however is best diagnosed with an ultrasound which is non-invasive test that can be done in the office.
Once a diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis is established further investigation is made by doing
- Weakness in arms or legs
- Difficulty speaking or getting words out or understanding speech
- Disorientation or difficulty with coordination
These tests further delineate the anatomy and the extent of the carotid arteries and guide us to specific treatments which includes:
- Open surgery
- Medical therapy
- Angioplasty
- Stent placement
Carotid artery disease treatment:
Carotid endarterectomy:
is an established and effective procedure in removing the atherosclerotic plaque from the carotid arteries, providing adequate blood flow to the brain and decreasing the chance of a stroke.
This procedure is done by making an incision in the neck at about 6 cm long. This procedure is done in the hospital under general anesthesia with microvascular techniques. It is usually taking about 2 hours and requires one day of hospitalization.
This is a well-established procedure that has been performed 100s of thousands of times with good results.
Carotid stenting:
this is a newer procedure which is minimally invasive to treat carotid stenosis.
During this procedure, access is established into the arterial system usually through the femoral artery in the groin. A guidewire is advanced into the carotid artery surgery followed by a balloon and stents which is deployed at the site of the obstruction to treat the obstruction and established flow to the brain. The procedure is done through a needle stick and there is no surgical incision required .
This is a minimally invasive procedure which is relatively new and its long-term efficacy is not has not been fully evaluated. This procedure is mainly done in patients that are not a good candidate for open carotid endarterectomy
At Encino Vascular Institute and vein center we and diagnose carotid stenosis with a carotid duplex and provide recommendations for invasive and noninvasive therapy for carotid stenosis.
Proudly accepting patients in