Health care
The Importance of Early Detection: How to Reduce Your Risk of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease is a condition that occurs when the carotid arteries, which are located on either side of the neck and supply blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to a stroke, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. In this article, we will discuss the importance of early detection of carotid artery disease and how to reduce your risk of developing this condition.
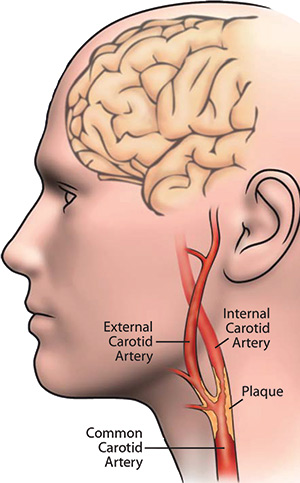
Understanding Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease occurs when plaque, a substance made up of fat,
cholesterol, and other materials, builds up in the walls of the carotid
arteries. This buildup can cause the arteries to become narrowed, which reduces
blood flow to the brain. In some cases, a blood clot can form in the narrowed
area, completely blocking blood flow to the brain and causing a stroke.
There are two types of carotid artery disease: symptomatic and asymptomatic.
Symptomatic carotid artery disease occurs when a person experiences symptoms
such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or
vision problems. Asymptomatic carotid artery disease, on the other hand, has no
symptoms and is often discovered during a routine medical exam or diagnostic
test.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
As previously mentioned, symptomatic carotid artery disease can cause a
variety of symptoms. These symptoms can include weakness or numbness on one
side of the body, difficulty speaking, vision problems, dizziness, and severe
headache. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek
medical attention immediately, as they may indicate a stroke.
Risk Factors for Carotid Artery Disease
There are several risk factors that can increase your likelihood of
developing carotid artery disease. These risk factors include:
The Importance of Early Detection
• Age: The risk
of carotid artery disease increases as you get older.
• Family history: If
you have a family history of carotid artery disease, you may be more likely to
develop the condition.
• High blood pressure:
High blood pressure can damage the walls of the carotid arteries and increase
the risk of plaque buildup.
• High cholesterol:
High levels of cholesterol in the blood can contribute to the buildup of plaque
in the carotid arteries.
• Smoking: Smoking
damages the walls of the carotid arteries and increases the risk of plaque
buildup.
Early detection of carotid artery disease is crucial for preventing a
stroke. If the condition is detected early, lifestyle changes and medications
may be effective in reducing plaque buildup and preventing a stroke. In some
cases, surgical or interventional treatments may be necessary to remove the
plaque and restore blood flow to the brain.
If you are at risk for carotid artery disease or experience any symptoms, it
is important to talk to your doctor about diagnostic tests. These tests may
include an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. Early detection can save your life and
prevent serious complications.
Diagnostic Tests for Carotid Artery Disease
There are several diagnostic tests that can be used to detect carotid artery
disease. These tests include:
• Ultrasound: This is
a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the carotid
arteries.
• CT scan: A CT scan
uses X-rays to create detailed images of the carotid arteries.
• MRI: An MRI uses
magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the carotid
arteries.
If carotid artery disease is detected, your doctor may recommend additional
tests to determine the severity of the condition and the best course of
treatment.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Your Risk
Making lifestyle changes can help reduce your risk of developing carotid
artery disease. These changes include:
• Quitting smoking:
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of
carotid artery disease.
• Eating a healthy
diet: A diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol can help reduce plaque
buildup in the carotid arteries.
• Exercising
regularly: Regular exercise can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk
of plaque buildup.
• Managing other
health conditions: Managing conditions such as high blood pressure, high
cholesterol, and diabetes can help reduce your risk of carotid artery disease.
Medications for Carotid Artery Disease
If you are diagnosed with carotid artery disease, your doctor may prescribe
medications to help reduce plaque buildup and prevent a stroke. These
medications may include:
• Statins: Statins are
a type of medication that can lower cholesterol levels in the blood and reduce
plaque buildup.
• Antiplatelet drugs:
Antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin, can help prevent blood clots from forming
in the carotid arteries.
• Blood pressure
medications: Medications that lower blood pressure can help reduce the risk of
plaque buildup in the carotid arteries.
Surgical and Interventional Treatments for
Carotid Artery Disease
In some cases, surgical or interventional treatments may be necessary to
remove plaque buildup and restore blood flow to the brain. These treatments
include:
• Carotid
endarterectomy: This is a surgical procedure that involves removing plaque from
the carotid arteries.
• Carotid artery
angioplasty and stenting: This is a minimally invasive procedure that involves
inserting a small tube into the carotid artery to remove plaque and improve
blood flow.
Your doctor will determine the best course of treatment based on the
severity of your condition and other factors.
Preventing Carotid Artery Disease Recurrence
If you have been diagnosed with carotid artery disease and have undergone
treatment, it is important to take steps to prevent a recurrence. These steps
include:
• Making lifestyle
changes: Continuing to make healthy lifestyle changes can help prevent the
recurrence of carotid artery disease.
• Taking medications:
Taking medications as prescribed by your doctor can help prevent the recurrence
of carotid artery disease.
• Regular follow-up
appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor can help monitor
your condition and detect any signs of recurrence.
Conclusion
Carotid artery disease is a serious condition that can lead to a stroke if
left untreated. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing
serious complications. If you are at risk for carotid artery disease or
experience any symptoms, talk to your doctor about diagnostic tests and
treatment options. By making lifestyle changes and following your doctor’s
recommendations, you can reduce your risk of developing carotid artery disease
and prevent a stroke.